Tuesday, March 23, 2010
Conduction is the transfer of energy through matter from particle to particle. It is the transfer and distribution of heat energy from atom to atom within a substance. For example, a spoon in a cup of hot soup becomes warmer because the heat from the soup is conducted along the spoon. Conduction is most effective in solids-but it can happen in fluids. Fun fact: Have you ever noticed that metals tend to feel cold? Believe it or not, they are not colder! They only feel colder because they conduct heat away from your hand. You perceive the heat that is leaving your hand as cold.
Radiation: Electromagnetic waves that directly transport ENERGY through space. Sunlight is a form of radiation that is radiated through space to our planet without the aid of fluids or solids. The energy travels through nothingness! Just think of it! The sun transfers heat through 93 million miles of space. Because there are no solids (like a huge spoon) touching the sun and our planet, conduction is not responsible for bringing heat to Earth. Since there are no fluids (like air and water) in space, convection is not responsible for transferring the heat. Thus, radiation brings heat to our planet.
Joanna

A pendulum is a weight suspended from a pivot so it can swing freely.[1]
When a pendulum is displaced from its resting equilibrium position, it is subject to a restoring force due to gravity that will accelerate it back toward the equilibrium position. When released, the restoring force combined with the pendulum's mass causes it to oscillate about the equilibrium position, swinging back and forth. The time for one complete cycle, a left swing and a right swing, is called the period. From its discovery around 1602 by Galileo Galilei the regular motion of pendulums was used for timekeeping, and was the world's most accurate timekeeping technology until the 1930s.[2] Pendulums are used to regulate pendulum clocks, and are used in scientific instruments such as accelerometers and seismometers. Historically they were used as gravimeters to measure the acceleration of gravity in geophysical surveys, and even as a standard of length. The word 'pendulum' is new Latin, from the Latin pendulus, meaning 'hanging'.[3]
The simple gravity pendulum[4] is an idealized mathematical model of a pendulum.[5] [6] [7] This is a weight (or bob) on the end of a massless cord suspended from a pivot, without friction. When given an initial push, it will swing back and forth at a constant amplitude. Real pendulums are subject to friction and air drag, so the amplitude of their swings declines.
-Amirul
 A micrometer (pronounced /mаɪˈkrɒmɨtər/, us dict: mī·krŏm′·ĭ·tər), sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device used widely in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades for precision measurement, along with other metrological instruments such as dial calipers and vernier calipers. Micrometers are often, but not always, in the form of calipers.
A micrometer (pronounced /mаɪˈkrɒmɨtər/, us dict: mī·krŏm′·ĭ·tər), sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge, is a device used widely in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades for precision measurement, along with other metrological instruments such as dial calipers and vernier calipers. Micrometers are often, but not always, in the form of calipers.-Rosabella (:
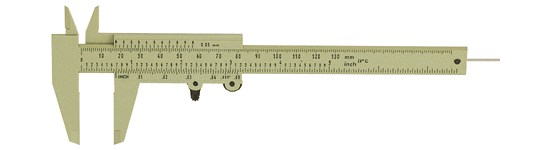
Instructions on use
- The Vernier caliper is an extremely precise measuring instrument; the reading error is 1/20 mm = 0.05 mm.
- Close the jaws lightly on the object to be measured.
- If you are measuring something with a round cross section, make sure that the axis of the object is perpendicular to the caliper. This is necessary to ensure that you are measuring the full diameter and not merely a chord.
- Ignore the top scale, which is calibrated in inches.
- Use the bottom scale, which is in metric units.
- Notice that there is a fixed scale and a sliding scale.
- The boldface numbers on the fixed scale are centimeters.
- The tick marks on the fixed scale between the boldface numbers are millimeters.
- There are ten tick marks on the sliding scale. The left-most tick mark on the sliding scale will let you read from the fixed scale the number of whole millimeters that the jaws are opened.
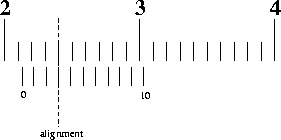
- In the example above, the leftmost tick mark on the sliding scale is between 21 mm and 22 mm, so the number of whole millimeters is 21.
- Next we find the tenths of millimeters. Notice that the ten tick marks on the sliding scale are the same width as nine ticks marks on the fixed scale. This means that at most one of the tick marks on the sliding scale will align with a tick mark on the fixed scale; the others will miss.
- The number of the aligned tick mark on the sliding scale tells you the number of tenths of millimeters. In the example above, the 3rd tick mark on the sliding scale is in coincidence with the one above it, so the caliper reading is (21.30 ± 0.05) mm.
- If two adjacent tick marks on the sliding scale look equally aligned with their counterparts on the fixed scale, then the reading is half way between the two marks. In the example above, if the 3rd and 4th tick marks on the sliding scale looked to be equally aligned, then the reading would be (21.35 ± 0.05) mm.
- On those rare occasions when the reading just happens to be a "nice" number like 2 cm, don't forget to include the zero decimal places showing the precision of the measurement and the reading error. So not 2 cm, but rather (2.000 ± 0.005) cm or (20.00 ± 0.05) mm.
-Caijun.

Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted from the surface of an object which is due to the object's temperature. An example of thermal radiation is the infrared radiation emitted by a common household radiator or electric heater. A person near a raging bonfire will feel the radiated heat of the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold. Thermal radiation is generated when heat from the movement of charged particles within atoms is converted to electromagnetic radiation. Solar radiation heats the earth during the day, while at night the earth re-radiates some heat back into space.
For more info go to, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermal_radiation
ADELINEE :D
this is a science physics blog.
if u wan to post,u can add related pictures,video.
Do not post any rubbish or stupid things here.
Byebye :D
Monday, March 22, 2010
Thermal radiation is electromagnetic radiation emitted from a material which is due to the heat of the material, the characteristics of which depend on its temperature. An example of thermal radiation is the infrared radiation emitted by a common household radiator or electric heater. A person near a raging bonfire will feel the radiated heat of the fire, even if the surrounding air is very cold. Thermal radiation is generated when heat from the movement of charges in the material (electrons and protons in common forms of matter) is converted to electromagnetic radiation. Sunshine, or solar radiation, is thermal radiation from the extremely hot gasses of the Sun, and this radiation heats the Earth. The Earth also emits thermal radiation, but at a much lower intensity because it is cooler. The balance between heating by incoming solar thermal radiation and cooling by the Earth's outgoing thermal radiation is the primary process that determines the Earth's overall temperature.
If the object is a black body in thermodynamic equilibrium, the radiation is termed black-body radiation[1]. The emitted wave frequency of the black body thermal radiation is described by a probability distribution depending only on temperature, and for a genuine black body in thermodynamic equilibrium is given by Planck’s law of radiation. Wien's law gives the most likely frequency of the emitted radiation, and the Stefan–Boltzmann law gives the radiant intensity.[2]
kaixian
MiraFateenNadia
The energy emitted by the sun passes through space until it is intercepted by planets, other celestial objects, or interstellar gas and dust। The intensity of solar radiation striking these objects is determined by a physical law known as the Inverse Square Law (Figure 3)। This law merely states that the intensity of the radiation emitted from the sun varies with the squared distance from the source. As a result of this law, if the intensity of radiation at a given distance is one unit, at twice the distance the intensity will become only one-quarter. At three times the distance, the intensity will become only one-ninth of its original intensity at a distance of one unit, and so on.
Labels: Physics
Convection is the movement of molecules within fluids (i.e. liquids, gases and rheids). It cannot take place in solids, since neither bulk current flows or significant diffusion can take place in solids.
Convection is one of the major modes of heat transfer and mass transfer. Convective heat and mass transfer take place through both diffusion – the random Brownian motion of individual particles in the fluid – and by advection, in which matter or heat is transported by the larger-scale motion of currents in the fluid. In the context of heat and mass transfer, the term "convection" is used to refer to the sum of adjective and diffusive transfer.[1]
Natural convective heat transfer
When heat is transferred by the circulation of fluids due to buoyancy from the density changes induced by heating itself, then the process is known as natural convection or free convection.
Familiar examples are the upward flow of air due to a fire or hot object and the circulation of water in a pot that is heated from below.
For a visual experience of natural convection, a glass that is full of hot water filled with red food dye may be placed inside a fish tank with cold, clear water. The convection currents of the red liquid will be seen to rise and also fall, then eventually settle, illustrating the process as heat gradients are dissipated.
chin ann



Convection is the transfer of heat by the actual movement of the warmed matter. Heat leaves the coffee cup as the currents of steam and air rise. Convection is the transfer of heat energy in a gas or liquid by movement of currents. (It can also happen is some solids, like sand.) The heat moves with the fluid. Consider this: convection is responsible for making macaroni rise and fall in a pot of heated water. The warmer portions of the water are less dense and therefore, they rise. Meanwhile, the cooler portions of the water fall because they are denser.
Conduction is the transfer of energy through matter from particle to particle. It is the transfer and distribution of heat energy from atom to atom within a substance. For example, a spoon in a cup of hot soup becomes warmer because the heat from the soup is conducted along the spoon. Conduction is most effective in solids-but it can happen in fluids. Fun fact: Have you ever noticed that metals tend to feel cold? Believe it or not, they are not colder! They only feel colder because they conduct heat away from your hand. You perceive the heat that is leaving your hand as cold.Radiation: Electromagnetic waves that directly transport ENERGY through space. Sunlight is a form of radiation that is radiated through space to our planet without the aid of fluids or solids. The energy travels through nothingness! Just think of it! The sun transfers heat through 93 million miles of space. Because there are no solids (like a huge spoon) touching the sun and our planet, conduction is not responsible for bringing heat to Earth. Since there are no fluids (like air and water) in space, convection is not responsible for transferring the heat. Thus, radiation brings heat to our planet.
Joanna
Vernier Calipers
The vernier scale is constructed so that it is spaced at a constant fraction of the fixed main scale. So for a decimal measuring device each mark on the vernier would be spaced nine tenths of those on the main scale. If you put the two scales together with zero points aligned then the first mark on the vernier scale will be one tenth short of the first main scale mark, the second two tenths short and so on up to the ninth mark which would be misaligned by nine tenths. Only when a full ten marks have been counted would there be an alignment because the tenth mark would be ten tenths, that is a whole main scale unit, short and will therefore align with the ninth mark on the main scale.
Now if you move the vernier by a small amount, say, one tenth of its fixed main scale, the only pair of marks which come into alignment will be the first pair since these were the only ones originally misaligned by one tenth. If we had moved it 2 tenths then the second pair and only the second would be in alignment since these are the only ones which were originally misaligned by that amount. If we had moved it 5 tenths then the fifth pair and only the fifth would be in alignment. And so on for any movement, only one pair of marks will be in alignment and that pair will show what is the value of the small displacement.
Nur Atiqah Nadia Binte Sukor
science 101 (theory of heat)
Convection is the transfer of heat by the actual movement of the warmed matter. Heat leaves the coffee cup as the currents of steam and air rise. Convection is the transfer of heat energy in a gas or liquid by movement of currents. (It can also happen is some solids, like sand.) The heat moves with the fluid. Consider this: convection is responsible for making macaroni rise and fall in a pot of heated water. The warmer portions of the water are less dense and therefore, they rise. Meanwhile, the cooler portions of the water fall because they are denser.

Radiation: Electromagnetic waves that directly transport ENERGY through space. Sunlight is a form of radiation that is radiated through space to our planet without the aid of fluids or solids. The energy travels through nothingness! Just think of it! The sun transfers heat through 93 million miles of space. Because there are no solids (like a huge spoon) touching the sun and our planet, conduction is not responsible for bringing heat to Earth. Since there are no fluids (like air and water) in space, convection is not responsible for transferring the heat. Thus, radiation brings heat to our planet.


Labels: Cody-Gene
heat transfer
enjoy watching it :P
Nadrah Irdina :P
Science(Physics)
Whenever there is aFRICTION and MOVEMENT between two objects , u'll get HEAT..
The reason is because , movement of MOLECULES and HEAT are really one and the same ,
bt we know that MOVEMENT is a form of ENERGY , so it follows that HEAT itself must
also be a form of ENERY..
That's why Heat , just like Energy , is measured in Joules.......................
In Heat Transfer :
= Conduvtion
= Convection
= Radiation
Nur Fazira =))

